淋巴瘤是一组起源于淋巴结和(或)结外部分淋巴组织的免疫细胞恶性肿瘤。其临床特征如下:
Lymphoma is a group of malignant tumors of immune cells originating from lymph nodes and/or extranodal lymphoid tissues. Its clinical features are as follows:
一、局部表现(Local Manifestations)
淋巴结肿大:较多患者在早期表现为无痛的颈部淋巴结肿大,以后其他部位陆续发现。淋巴结可从黄豆大到枣大,中等硬度,坚韧,均匀,丰满。一般与皮肤无粘连,在初期和中期互不融合,可活动。后期可互相融合成大块,直径可达20cm以上,侵犯皮肤,破溃后经久不愈。
Lymphadenopathy:Many patients present with painless cervical lymphadenopathy in the early stage, and subsequently, lymph nodes in other parts of the body are found. The lymph nodes can range from the size of a soybean to a date, with medium hardness, firmness, uniformity, and fullness. They are generally not adhered to the skin and are movable in the early and middle stages. In the later stages, they can fuse into large masses with diameters exceeding 20cm, invading the skin and failing to heal for a long time after rupture.
纵膈:好发部位之一。多数患者初期无明显症状,主要表现为X光片上有中纵膈和前纵膈的分叶状阴影。有的患者可有急剧发展的上腔静脉压迫症或气管、食管、膈神经受压的表现。
Mediastinum:The mediastinum is one of the common sites of involvement. Most patients have no obvious symptoms in the initial stage, and the main manifestation is lobulated shadows in the middle and anterior mediastinum on X-ray films. Some patients may have rapidly progressing superior vena cava syndrome or compression of the trachea, esophagus, and phrenic nerve.
肝与脾:原发性肝恶性淋巴瘤少见,继发侵犯肝脏的并不少见,部分病例可以肝脾肿大为首发症状。发生于脾的恶性淋巴瘤预后较好,有肝受侵的预后不佳。
Liver and Spleen:Primary malignant lymphoma of the liver is rare, but secondary invasion of the liver is not uncommon. In some cases, hepatosplenomegaly can be the initial symptom. The prognosis of malignant lymphoma originating in the spleen is better, while that with liver invasion is poor.
结外器官:罕见情况下HD有结外器官如骨、咽淋巴环、皮肤、消化道、脑等的浸润。
Extranodal Organs:In rare cases, HD can infiltrate extranodal organs such as bones, the Waldeyer's ring, skin, digestive tract, brain, etc.
二、全身表现(Systemic Manifestations)
全身症状:约10%的患者可以发热、发痒、盗汗及消瘦等全身症状为最早出现的临床表现。有的患者会出现长期不规则的原因不明的发热,经2年以上始发现表浅淋巴结肿大放得确诊。
Systemic Symptoms:About 10% of patients may present with systemic symptoms such as fever, itching, night sweats, and weight loss as the earliest clinical manifestations. Some patients may experience long-term irregular and unexplained fever, and superficial lymphadenopathy is found after more than two years before diagnosis.
皮肤病变:患者可有一系列的非特异性皮肤表现,常见的是糙皮病样丘疹、带状疱疹、全身疱疹样皮炎、色素沉着及剥脱样皮炎。晚期淋巴瘤患者免疫状况低下,皮肤感染常经久破溃、渗液,形成全身性散在的皮肤增厚、脱屑。
Skin Lesions:Patients may have a series of nonspecific skin manifestations, commonly including pellagra-like papules, herpes zoster, generalized herpesiform dermatitis, pigmentation, and exfoliative dermatitis. In late-stage lymphoma patients with compromised immune status, skin infections often persist with ulceration and exudation, resulting in generalized skin thickening and desquamation.
贫血:约10%-20%的患者在就诊时已经有贫血症状,甚至可发生于淋巴结肿大前几个月,晚期患者更甚。
Anemia:About 10%-20% of patients have anemia at the time of diagnosis, which may even occur several months before lymph node enlargement, and is more severe in late-stage patients.
神经系统表现:患者可有一系列非特异性皮肤表现,如进行性多灶性脑白质病、亚急性坏死性脊髓病、感觉或运动性周围神经病变以及多发性肌病等。
Neurological Manifestations:Patients may have a series of nonspecific neurological manifestations, such as progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy, subacute necrotizing myelitis, sensory or motor peripheral neuropathy, and polymyositis.
免疫功能低下:由于患者免疫状况低下,可发生神经系统感染,如新型隐球菌等,也可发生血源性化脓性脑膜炎或脑脓肿。恶性淋巴瘤侵犯脑实质可伴发脑出血。
Immunodeficiency:Due to immunodeficiency, patients may develop neurological infections such as Cryptococcus neoformans, as well as blood-borne pyogenic meningitis or brain abscesses. Malignant lymphoma invading the brain parenchyma can be accompanied by cerebral hemorrhage.
病例解析(Case Analysis)
患者信息:58岁,男性
诊 断:2012年7月发现右腋下肿大,同年8月21日诊断出肿瘤直径为8CM。医院诊断为恶性淋巴瘤(滤泡性)。同年9月开始抗癌治疗,3个月后未见改善,同时悸动、气短等副作用明显。同年12月再次检查,施行细胞免疫治疗。
治疗情况:患者经过6次NK细胞免疫治疗后,癌巢明显缩小。
Patient Information):58-year-old male
Diagnosis:In July 2012, a right axillary enlargement was found, and on August 21 of the same year, a tumor with a diameter of 8cm was diagnosed. The hospital diagnosed it as malignant lymphoma (follicular). Anticancer treatment was initiated in September of the same year, but there was no improvement after 3 months, and side effects such as palpitations and shortness of breath were evident. In December of the same year, the patient underwent re-examination and cellular immunotherapy was administered.
Treatment:After six NK cell immunotherapies, the cancer nest significantly shrunk.
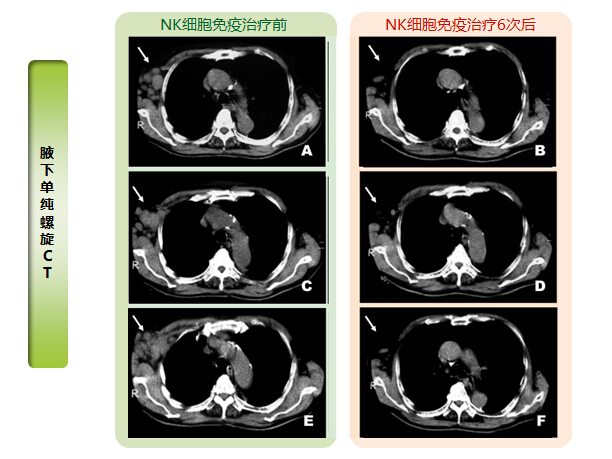
治疗前后对比(Comparison Before and After Treatment)
治疗前:悸动、气短等副作用明显
Before Treatment:Obvious side effects such as palpitations and shortness of breath
治疗后:副作用消失,肿块明显减小
After Treatment:Side effects disappeared, and the tumor significantly reduced
经验分享:NK细胞属于自体免疫细胞,治疗过程无副作用。在此病例中,NK细胞免疫疗法对于恶性淋巴瘤起到了很好的治疗效果,并且同时改善了患者的免疫功能,提高了自体抗癌能力。
Experience Sharing:NK cells are autologous immune cells with no side effects during treatment. In this case, NK cell immunotherapy had a good therapeutic effect on malignant lymphoma and simultaneously improved the patient's immune function, enhancing their autologous anticancer ability.