然而,随着生物医学技术的进步,干细胞外泌体作为一种新兴的治疗策略,正逐渐为眼科疾病治疗带来突破。
However, advancements in biomedical technology - particularly stem cell-derived exosomes - are emerging as a promising therapeutic strategy for ophthalmic diseases.
外泌体是一种天然存在于细胞外的小囊泡,能携带蛋白质、RNA和其他分子,在细胞之间传递信息。在眼科医学中,外泌体特别是干细胞来源的外泌体,已被用于治疗多种眼部疾病,包括青光眼、角膜损伤、糖尿病视网膜病变和老年性黄斑变性等。
Exosomes are naturally occurring extracellular vesicles that transport proteins, RNA, and other molecules between cells. In ophthalmology, exosomes - especially those derived from stem cells - have been applied in treating various eye conditions, including glaucoma, corneal injury, diabetic retinopathy, and age-related macular degeneration.
干细胞外泌体治疗眼科疾病的机制
Mechanisms of Stem Cell Exosomes in Ophthalmic Therapies
1、促进组织修复与再生Tissue Repair & Regeneration
通过携带促生长因子等有益分子,干细胞外泌体可以促进角膜和视网膜等组织的修复,特别是在视网膜退行性变、角膜损伤等疾病中显示出积极的治疗效果。
By delivering growth-promoting factors and other beneficial molecules, stem cell exosomes facilitate repair of corneal and retinal tissues. They have demonstrated positive therapeutic effects in conditions like retinal degeneration and corneal injury.
2、抗炎作用Anti-Inflammatory Effects
在眼科一些由免疫引起的疾病中,如干眼症、角膜炎等,外泌体能够调节免疫系统,减少炎症反应,从而减轻炎症症状并促进局部免疫环境的恢复。
In immune-mediated eye diseases like dry eye syndrome and keratitis, exosomes regulate immune responses, reduce inflammation, alleviate symptoms, and restore local immune balance.
3、减少纤维化与疤痕形成Fibrosis & Scarring Reduction
在眼科手术后,纤维化和疤痕形成是常见的并发症,它们不仅影响术后效果,还可能导致视力进一步下降。而外泌体能够通过抑制成纤维细胞的活性,减少这些并发症的发生,促进更为理想的愈合过程。
Fibrosis and scarring are common post-operative complications in ophthalmology that impair surgical outcomes and worsen vision. Exosomes inhibit fibroblast activity, reducing these complications and promoting optimal healing.
4、精准靶向递送Precise Targeted Delivery
能够精准地将治疗分子送至病变部位。结合基因编辑技术和纳米技术,外泌体的靶向递送系统能够进一步提高疗效,减少副作用。研究表明,干细胞外泌体能够靶向作用于视网膜的微血管,显著减轻血管渗漏,促进视网膜的血流恢复[1,2]。
Exosomes can precisely deliver therapeutic molecules to diseased sites. When combined with gene editing and nanotechnology, their targeted delivery systems enhance efficacy while minimizing side effects. Studies show stem cell exosomes target retinal microvasculature, significantly reducing vascular leakage and restoring retinal blood flow[1,2].
干细胞外泌体治疗青光眼
Stem Cell Exosomes in Glaucoma Treatment
青光眼的发生往往与眼内压异常升高紧密相关,持续的高压环境导致视网膜神经节细胞(RGCs)受损乃至丧失,最终引发失明。因此,探索有效手段以减轻RGCs损害,对于青光眼的治疗与失明预防至关重要。
Glaucoma development is closely linked to abnormally elevated intraocular pressure (IOP). Prolonged high pressure damages and kills retinal ganglion cells (RGCs), leading to blindness. Therefore, developing effective methods to protect RGCs is critical for glaucoma treatment and blindness prevention.
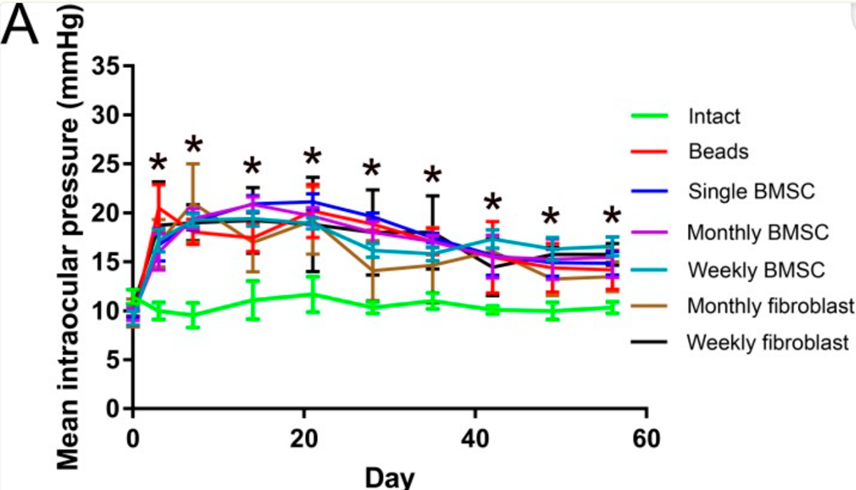
一项研究[3]聚焦于间充质干细胞衍生的外泌体在青光眼治疗中的潜力。研究团队构建了青光眼大鼠模型,并将其分为三组:健康对照组(5只大鼠)、青光眼模型实验组A(30只大鼠,通过前房内微珠植入诱导眼内压升高)和青光眼模型实验组B(35只大鼠,采用小梁网激光凝固术造成眼内压上升)。
A study[3] investigated the potential of mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes in glaucoma treatment. Researchers created glaucoma rat models divided into three groups: healthy controls (5 rats), experimental group A (30 rats with IOP elevation via anterior chamber microbead implantation), and experimental group B (35 rats with IOP elevation via trabecular meshwork laser coagulation).
实验组A与B的大鼠分别接受了每周或每月一次的玻璃体内注射,注射物为间充质干细胞衍生的外泌体或作为对照的成纤维细胞外泌体。
Rats in groups A and B received either weekly or monthly intravitreal injections of mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes or control fibroblast-derived exosomes.
研究结果显示,无论是每周还是每月的注射频率,间充质干细胞衍生的外泌体均展现出了对RGCs的神经保护作用,为青光眼的治疗提供了新的研究方向。
Results showed that mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes - regardless of injection frequency - provided significant neuroprotection for RGCs, offering a new research direction for glaucoma treatment.
干细胞外泌体作为一种新兴的治疗工具,正逐步在眼科领域展现出其广阔的应用前景。虽然目前仍处于临床研究阶段,但通过不断的技术进步和临床验证,干细胞外泌体有望为眼科疾病治疗带来革命性的突破。我们期待,未来能够看到更多的临床成果,为全球眼科患者带来新的希望!
As an emerging therapeutic tool, stem cell exosomes are demonstrating broad application potential in ophthalmology. While still in clinical research phases, continued technological advancements and validation hold promise for revolutionary breakthroughs in eye disease treatments. We anticipate seeing more clinical successes that bring new hope to patients worldwide!
参考文献:
[1] Harrell CR, Djonov V, Volarevic V. Therapeutic Potential of Mesenchymal Stem Cells in the Treatment of Ocular Graft-Versus-Host Disease. Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Oct 31;23(21):13254. doi: 10.3390/ijms232113254. PMID: 36362040; PMCID: PMC9656879.
[2]Harrell CR, Volarevic V, Djonov V, Volarevic A. Therapeutic Potential of Exosomes Derived from Adipose Tissue-Sourced Mesenchymal Stem Cells in the Treatment of Neural and Retinal Diseases. Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Apr 19;23(9):4487. doi: 10.3390/ijms23094487. PMID: 35562878; PMCID: PMC9105552.
[3] Mead B, Amaral J, Tomarev S. Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Small Extracellular Vesicles Promote Neuroprotection in Rodent Models of Glaucoma. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2018 Feb 1;59(2):702-714. doi: 10.1167/iovs.17-22855. PMID: 29392316; PMCID: PMC5795911.