As we all know, the human body houses a mysterious yet powerful "health protection squad" - the immune system.
众所周知,身体里有一支神秘又强大的 “健康护卫队”,那就是免疫系统。
近期,北京协和医院的一项重要研究揭开了免疫系统的神秘面纱,通过对1068名健康中国成年人免疫细胞分布和变化的深入分析,展示了人体免疫系统在不同年龄阶段的运行逻辑。
A recent landmark study by Peking Union Medical College Hospital has lifted the veil on this system. Through in-depth analysis of immune cell distribution and changes in 1,068 healthy Chinese adults, it revealed the operational logic of the human immune system across different age groups.
这一研究成果意义非凡,不仅为医学研究提供了重要参考,也为普通人提供了关于健康管理的新视角。
This groundbreaking research holds significant implications, providing both medical researchers with critical references and the general public with new perspectives on health management.

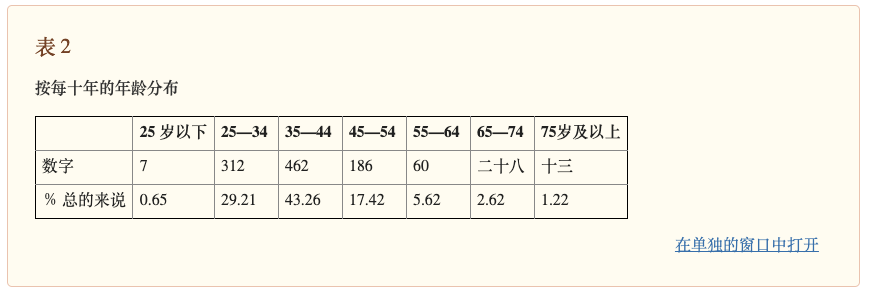
该研究共招募了1068例年龄在18~80岁之间的中国志愿者,平均年龄为40.5岁,其中青年组781人(19~44岁,平均年龄35.4岁),中年组246人(45~64岁,平均年龄50.9岁),老年人组41人(65~80岁,平均年龄71.6岁)。
The study recruited 1,068 Chinese volunteers aged 18-80 (mean age 40.5), divided into three groups: 781 youth (19-44, mean 35.4), 246 middle-aged (45-64, mean 50.9), and 41 elderly (65-80, mean 71.6).
研究发现,19~44岁是人体免疫系统的黄金时期,这一阶段的淋巴细胞犹如充满活力的战士,随时准备和外界的病菌“大战一场”。这时候淋巴细胞平均计数高达2086 cells/µl,CD19+ B细胞与CD3+CD4+ T细胞比例均衡,展现出全面而强大的免疫能力。
Findings showed that 19-44 years represents the immune system's prime. Lymphocytes at this stage act like energetic warriors ready to combat external pathogens. Average lymphocyte counts reached 2086 cells/µl, with balanced CD19+ B cells and CD3+CD4+ T cells reflecting comprehensive immune strength.
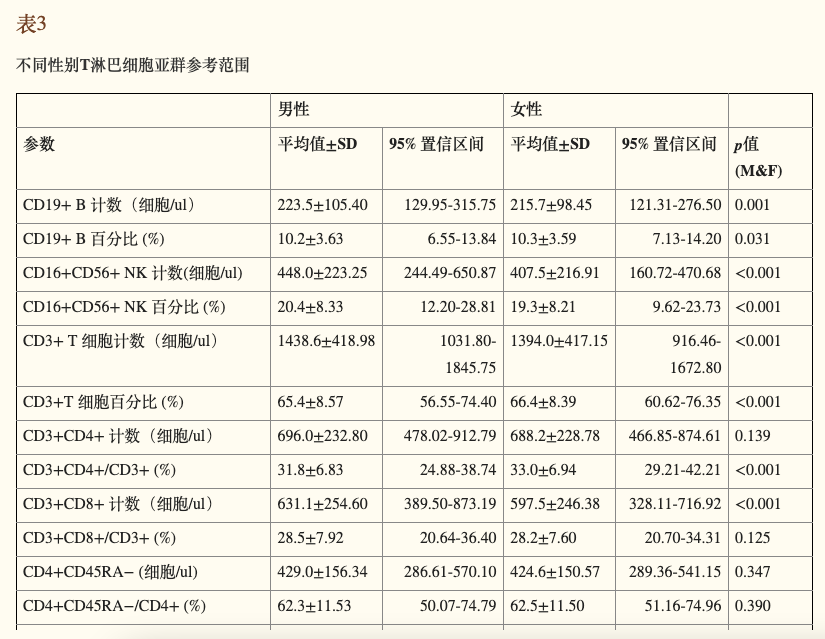
尽管这个阶段的男性和女性虽然免疫细胞总数有点差异,但免疫细胞的分布和功能趋于一致。无论是快速应对病毒入侵,还是对抗细菌感染,年轻组的免疫系统都堪称高效且精锐。
Although slight differences in total immune cell counts existed between genders, distribution and function remained consistent. The young group's immune system demonstrated high efficiency and precision in responding to viral invasions and bacterial infections.
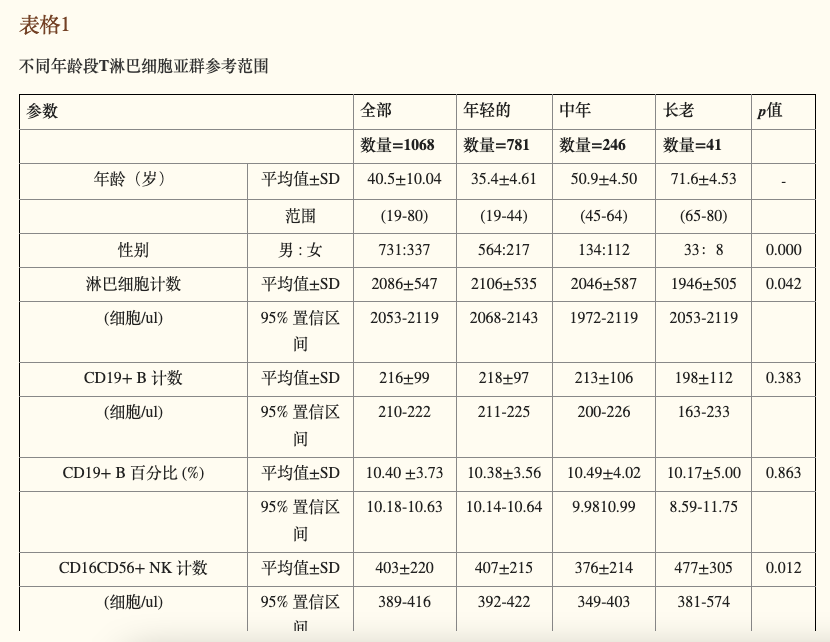
随着年龄增长,人体进入45~64岁的中年阶段。这一阶段的免疫系统就像历经风霜的老兵,虽然淋巴细胞的平均计数略微下降至2046 cells/µl,但免疫功能却更加成熟稳重。CD19+ B 细胞和 CD3+CD4+ T 细胞数量没明显变化,可它们在面对威胁时更精准了,就像经验丰富的猎手,不再盲目出击,而是选择最优策略,减少不必要的“内耗”。在这一阶段,男性和女性之间的免疫表现开始显现细微差别。研究指出,男性免疫细胞的数量和活性在压力下较易波动,而女性在同样条件下则表现出更高的稳定性。
As age progresses to 45-64, the immune system resembles a seasoned veteran. While average lymphocyte counts slightly decreased to 2046 cells/µl, immune function became more mature. CD19+ B and CD3+CD4+ T cell counts remained stable but became more precise in threat responses - like experienced hunters choosing optimal strategies to minimize unnecessary energy expenditure. Subtle gender differences emerged: male immune cell counts and activity fluctuated more under stress, while females showed greater stability.
到了65~80岁的老年阶段,人体免疫系统的战斗力虽然减弱了,却依然是健康防线的中流砥柱。老年组平均淋巴细胞计数下降至1946 cells/µl,然而,即便在“兵力”减少的情况下,CD19+ B 细胞与 CD3+CD4+ T 细胞还是认真履行职责。NK 细胞数量虽然下降了,可精准打击能力还在,就像精简的特种部队,依然能对抗病毒和肿瘤威胁。另外,研究还发现,虽然免疫功能随年龄衰退是自然规律,但通过外界干预,免疫力的下降速度或许可以放缓。例如,适当补充NK细胞或改善其活性,可能有效延缓衰老和疾病的发生。
In the 65-80 age group, while immune strength diminishes, it remains a vital health defender. Average lymphocyte counts dropped to 1946 cells/µl, yet CD19+ B and CD3+CD4+ T cells continued performing their roles. Although NK cell numbers decreased, their precision strike capabilities remained intact - like elite special forces still combating viral and tumor threats. Significantly, while immune decline is natural, external interventions like NK cell supplementation or activation enhancement may slow this process, potentially delaying aging and disease onset.
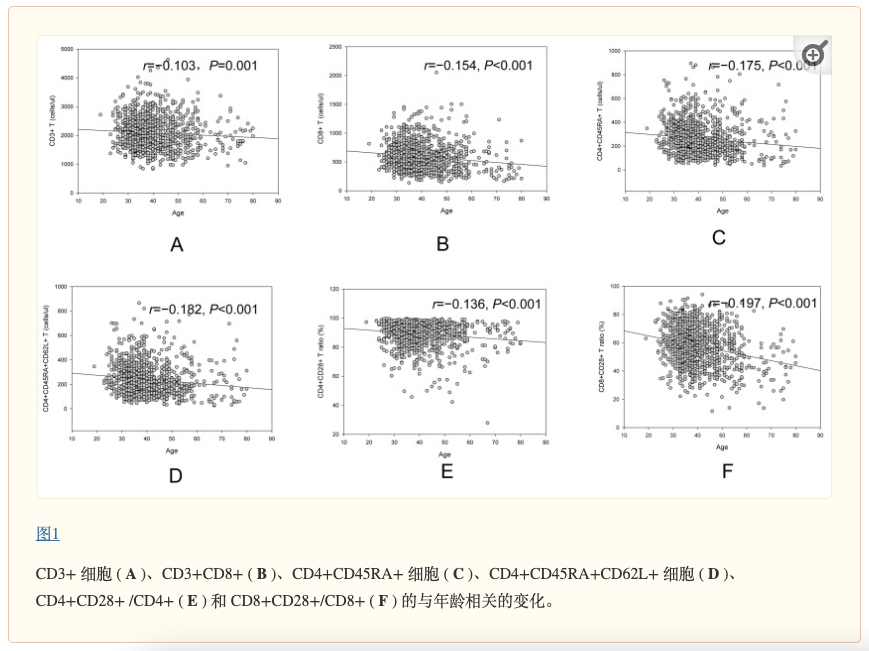
研究中特别提到NK细胞的作用,这些“隐形卫士”是免疫系统中最重要的组成部分之一。它们能迅速识别并清除被感染的细胞和癌细胞,是抵御疾病的第一道屏障。
The study highlighted NK cells as critical "invisible guardians" in immune defense. These cells rapidly identify and eliminate infected and cancerous cells, serving as the first line of disease defense. Their performance varies across ages:
在不同年龄段,NK细胞表现也不一样:
年轻时,活跃又高效,堪称“尖兵部队”;
中年时,总量略有下降,但精准性和稳定性达到巅峰;
老年时,数量和活性双双下滑,但依然承担着重要职责。
Youth: Active and efficient "elite troops"
Middle age: Slight numerical decline but peak precision/stability
Old age: Reduced quantity/activity but continued vital roles
研究还发现,通过外源性输注NK细胞,能给免疫系统补充“火力”,弥补不足。在抗癌、抗感染方面,这项技术已经展现出潜力,也为治疗衰老和免疫系统疾病提供了新方向。
Additionally, exogenous NK cell infusion was shown to replenish immune "firepower" and address deficiencies. This technology has demonstrated potential in cancer/anti-infection therapies and offers new directions for treating aging and immune disorders.
北京协和医院的这项研究,不仅是一次科学领域的突破,也为每个人提供了关于自身健康的宝贵启示。免疫系统的强大与否,直接决定了我们的生活质量和寿命长短。
This Peking Union Medical College Hospital study represents both a scientific breakthrough and a valuable health guide. The strength of our immune system directly influences quality of life and lifespan.
从青春期到老年期,免疫系统的变化就像人生的写照:青春期活力满满,免疫细胞数量多;中年期沉稳高效,注重免疫效率;老年期虽然“兵力”减少,但依然顽强抵抗。
From adolescence to old age, immune system changes mirror life's journey:
Adolescence: Vigorous with abundant immune cells
Middle age: Steady and efficient, prioritizing immune effectiveness
Old age: Reduced "troops" but persistent resistance
那我们该怎么根据这个研究结果来守护自己的免疫系统呢?年轻人要注重提升NK细胞活性,保持健康的生活习惯;中年人可以通过科学饮食和适当运动维持免疫系统的稳定;老年人则可以结合外源性干预,比如输注NK细胞,来减缓免疫衰退。
How can we apply these findings? Youth: Enhance NK cell activity through healthy lifestyles.Middle-aged: Maintain immune stability via scientific diet/exercise.Elderly: Consider exogenous interventions like NK cell infusions to slow immune decline.
未来,提升免疫力的方法会越来越多,无论是输注细胞,还是激活体内免疫机制,健康长寿不再是遥不可及的梦。让我们用科学的方法为免疫系统“加油”,拥抱更健康的生活!
The future holds increasing immunity-boosting options - from cell infusions to activating endogenous mechanisms - making healthy longevity a realistic goal. Let's "refuel" our immune systems scientifically and embrace healthier lives!